Running miniDC/OS (Mesosphere, Marathon, DCOS, and Docker containers) locally via Docker
In this post I’ll outline steps to run miniDC/OS locally via Docker. miniDC/OS provides a container orchestration platform you can run locally for development/testing purposes, built using Apache Mesos, Marathon, Mesosphere’s Datacenter Operating System (DC/OS), and Docker containers. This post was developed using a Mac running OSX and Docker for Mac.
Part 1: miniDC/OS installation
Initial installation via Homebrew.
# check docker version
docker --version
Docker version 18.09.2, build 6247962
# NOTE: I bumped up docker's available memory to 8GB
# install python
brew install python
brew postinstall python
# install minidcos
brew install https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dcos/dcos-e2e/master/minidcos.rb
# check for issues with doctor command
minidcos docker doctorChecking network setup.
minidcos docker setup-mac-network
# NOTE: I followed the steps to install Tunnelblick for OpenVPN
# URL: https://tunnelblick.net/
# Latest stable version at the time was 3.7.8
# opened OpenVPN docker-for-mac configuration file
open /Users/eric/Documents/docker-for-mac.ovpn
# Clicked on Tunnelblick in task bar, and choose Connect docker-for-mac
# re-executed:
minidcos docker setup-mac-network
# re-executed to check for issues:
minidcos docker doctorCreate local DCOS cluster.
# Download DCOS installer
minidcos docker download-installer
# create cluster (note: newline)
minidcos docker create ./dcos_generate_config.sh --agents 2
default
# wait for cluster
minidcos docker wait
# list (docker) clusters
minidcos docker list
default
# inspect dcos cluster
minidcos docker inspect
{
"Cluster ID": "default",
"DC/OS Variant": "OSS",
"Nodes": {
"agents": [
{
"docker_container_id": "052111ef91e53f26c8ff0d3f5a1af09f926d0f956b1417d834445034207a3184",
"docker_container_name": "dcos-e2e-default-3f4e1-agent-1",
"e2e_reference": "agent_1",
"ip_address": "172.17.0.5"
},
{
"docker_container_id": "676cef1b6f9decb25045363f1021bdd7dd84213bedcd8ef38e063be389c408c8",
"docker_container_name": "dcos-e2e-default-3f4e1-agent-0",
"e2e_reference": "agent_0",
"ip_address": "172.17.0.4"
}
],
"masters": [
{
"docker_container_id": "5729757089b43507e9b72efd436aa7fd887017bedd0e11a2428b366940f0cf6b",
"docker_container_name": "dcos-e2e-default-3f4e1-master-0",
"e2e_reference": "master_0",
"ip_address": "172.17.0.3"
}
],
"public_agents": [
{
"docker_container_id": "712acc52c1725d607d097b66841e87784c480b5d363c3212ca380f31ab6a0eef",
"docker_container_name": "dcos-e2e-default-3f4e1-public-agent-0",
"e2e_reference": "public_agent_0",
"ip_address": "172.17.0.6"
}
]
},
"SSH key": "/var/folders/4j/wfxggd095pv_dlb6d0zhwhdc0000gn/T/4194cb568a514f12837d5cbc3d9b3123/ssh/id_rsa",
"Web UI": "http://172.17.0.3"
}
# run inspect command formatted for environment variables
minidcos docker inspect --env --cluster-id default
export MASTER_0=5729757089b43507e9b72efd436aa7fd887017bedd0e11a2428b366940f0cf6b
export MASTER_0_IP=172.17.0.3
export AGENT_1=052111ef91e53f26c8ff0d3f5a1af09f926d0f956b1417d834445034207a3184
export AGENT_1_IP=172.17.0.5
export AGENT_0=676cef1b6f9decb25045363f1021bdd7dd84213bedcd8ef38e063be389c408c8
export AGENT_0_IP=172.17.0.4
export PUBLIC_AGENT_0=712acc52c1725d607d097b66841e87784c480b5d363c3212ca380f31ab6a0eef
export PUBLIC_AGENT_0_IP=172.17.0.6
export WEB_UI=http://172.17.0.3
export SSH_KEY=/var/folders/4j/wfxggd095pv_dlb6d0zhwhdc0000gn/T/4194cb568a514f12837d5cbc3d9b3123/ssh/id_rsa
# export/load environment variables into current shell
eval $(minidcos docker inspect --env --cluster-id default)
# ssh to master node
docker exec -it $MASTER_0 bash
# ssh to agent node
docker exec -it $AGENT_0 bash
# show created docker containers
docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
a69d40cc7e77 dcos-e2e/openvpn "/local/helpers/run.…" 23 minutes ago Up 23 minutes vpn-dcos-e2e-openvpn
4babdda6a6f0 dcos-e2e/proxy "socat TCP-LISTEN:13…" 23 minutes ago Up 23 minutes 127.0.0.1:13194->13194/tcp vpn-dcos-e2e-proxy
d40375eb092a mesosphere/dcos-docker "/sbin/init" 17 hours ago Up 17 hours dcos-e2e-default-45e4c-public-agent-0
05750b6a6657 mesosphere/dcos-docker "/sbin/init" 17 hours ago Up 17 hours dcos-e2e-default-45e4c-agent-1
390c367a5c71 mesosphere/dcos-docker "/sbin/init" 17 hours ago Up 17 hours dcos-e2e-default-45e4c-agent-0
cbaa0b009787 mesosphere/dcos-docker "/sbin/init" 17 hours ago Up 17 hours dcos-e2e-default-45e4c-master-0
# run a command (bash) to test
minidcos docker run bash
[root@dcos-e2e-default-45e4c-master-0 /]# exit
exit
# run Mesosphere DC/OS web interface
minidcos docker webAt this point, the web interface should be accessible (ex: http://172.17.0.3), but you will need to authenticate using the dcos cli.
Part 2: DCOS CLI and cluster setup
Install the DCOS CLI tool via Homebrew and setup the DCOS instance.
# install CLI tool
brew install dcos-cli
# setup DCOS cluster
# NOTE: you will need to follow the auth0/oauth login/redirection
dcos cluster setup http://172.17.0.3
# show cluster name
dcos config show cluster.name
DCOS
# list clusters
dcos cluster list
NAME CLUSTER ID STATUS VERSION URL
DCOS* 21538fe8-23fc-4e7c-9749-2c1b77935b4c AVAILABLE 1.12.2 http://172.17.0.3
# (optional) if you have multiple clusters, you can attach one by its name
dcos cluster attach DCOS
# list dcos nodes
dcos node
HOSTNAME IP ID TYPE REGION ZONE
172.17.0.4 172.17.0.4 c0720123-b041-44b7-bc8f-87ada5a10a69-S2 agent None None
172.17.0.5 172.17.0.5 c0720123-b041-44b7-bc8f-87ada5a10a69-S1 agent None None
172.17.0.6 172.17.0.6 c0720123-b041-44b7-bc8f-87ada5a10a69-S0 agent None None
master.mesos. 172.17.0.3 c0720123-b041-44b7-bc8f-87ada5a10a69 master (leader) None NoneAt this point you should be able authenticate to the web interface.
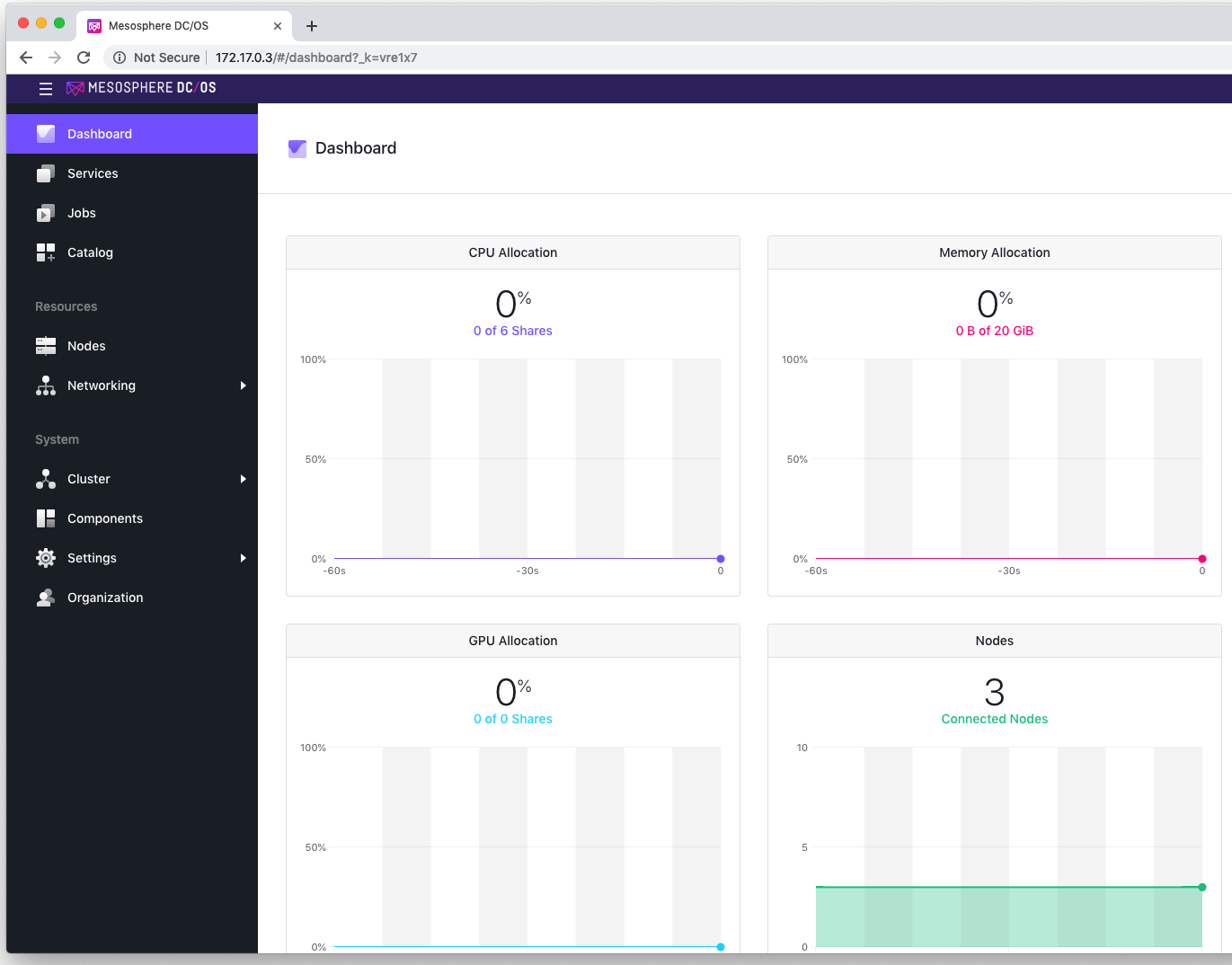
Mesosphere DC/OS Dashboard:
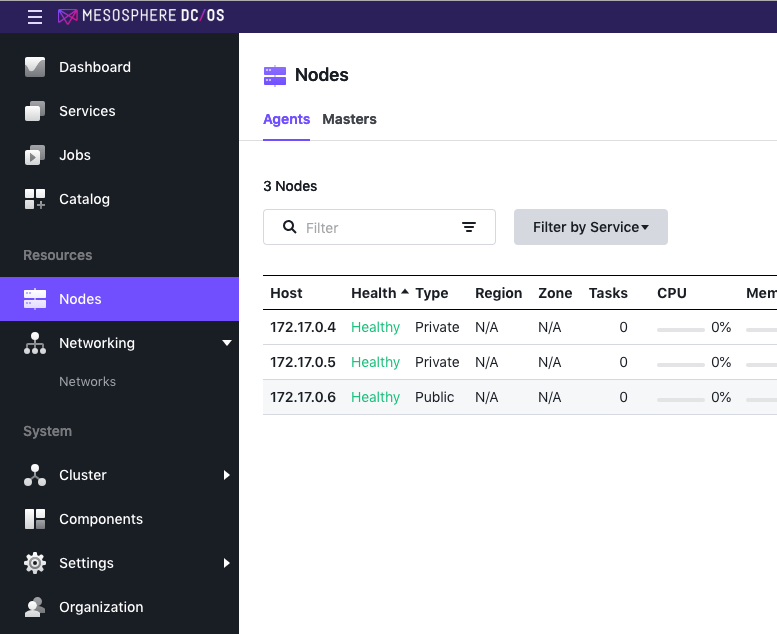
Show nodes:
In addition, telemetry URL and health report: http://172.17.0.3/system/health/v1/report
Part 3: Spark package installation
I used Spark to demonstrate installing a package.
# list repos
dcos package repo list
Universe: https://universe.mesosphere.com/repo
# search for a package (spark)
dcos package search spark | head -2
NAME VERSION SELECTED FRAMEWORK DESCRIPTION
spark 2.6.0-2.3.2 True False Spark is a fast and general cluster computing system for Big Data. Documenta...
# install spark
dcos package install spark --yes
Installing Marathon app for package [spark] version [2.6.0-2.3.2]
Installing CLI subcommand for package [spark] version [2.6.0-2.3.2]
# list packages
dcos package list
NAME VERSION APP COMMAND DESCRIPTION
spark 2.6.0-2.3.2 /spark spark Spark is a fast and general cluster computing system for Big...
# list services
dcos service
NAME HOST ACTIVE TASKS CPU MEM DISK ID
marathon 172.17.0.3 True 1 1.0 1024.0 0.0 c0720123-b041-44b7-bc8f-87ada5a10a69-0001
metronome 172.17.0.3 True 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 c0720123-b041-44b7-bc8f-87ada5a10a69-0000
spark dcos-e2e-default-3f4e1-agent-0 True 0 0.0 0.0 0.0 c0720123-b041-44b7-bc8f-87ada5a10a69-0002
# list tasks
dcos task
NAME HOST USER STATE ID MESOS ID REGION ZONE
spark 172.17.0.4 root R spark.08077572-387b-11e9-ab43-70b3d5800003 c0720123-b041-44b7-bc8f-87ada5a10a69-S2 --- ---
# get dcos spark webui
http://172.17.0.3/service/spark/ui
# run spark job
dcos spark run --submit-args="--class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi https://downloads.mesosphere.com/spark/assets/spark-examples_2.11-2.0.1.jar 30"
# output spark driver logs
dcos spark log driver-20190224213230-0001
[bind-address]: Resolving container IP to bind to using detection method:
[bind-address]: Resolution method is not specified, using the default 'hostname=ip-address'
[bind-address]: Bind address: 172.17.0.5
spark-env: StatsD metrics require Mesos UCR. For dispatcher metrics, enable the 'UCR_containerizer' option. For driver metrics, include '--conf spark.mesos.containerizer=mesos' in your run
Pi is roughly 3.140829046943016
# review mesos/marathon internal DNS
# SSH to agent node:
docker exec -it $AGENT_0 bash
# dig spark service
dig +noall +answer spark.marathon.mesos
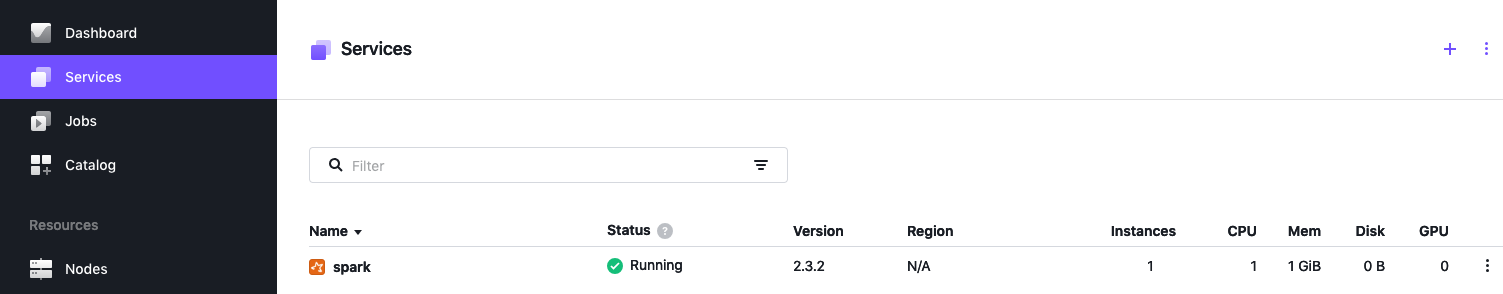
spark.marathon.mesos. 60 IN A 172.17.0.4Viewing Spark from the services page
The Marathon UI can be accessed directly or from the services page
Example URLs:
http://172.17.0.3/service/marathon/ui/#/apps
http://172.17.0.3:8080/ui/#/apps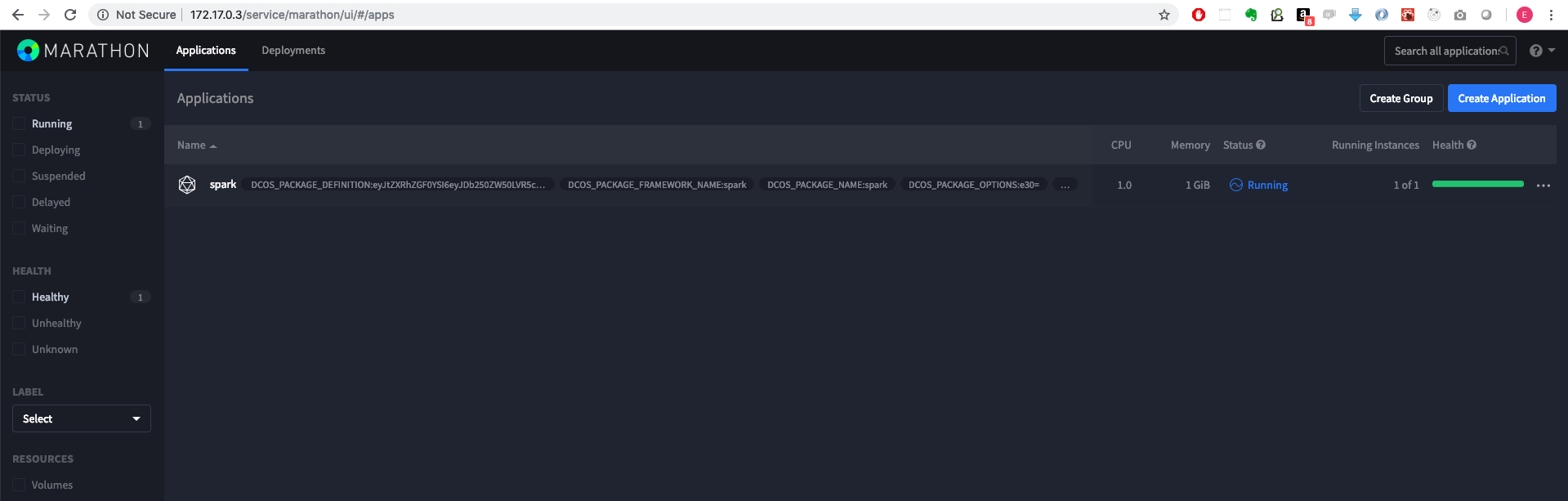
Part 4: Deploying a Marathon Pod
To demonstrate deploying a Marathon Pod I created 3 containers (Rails API, Postgresql, and Nginx). I put the full source code for these containers on GitHub. I also provided a docker-compose file to test the container connectivity outside DCOS/Marathon.
I created a script to build each Docker container, tag, and push to Docker Hub. file: rails-stack/build-images.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
DOCKER_USER=$1
if [ -z "$DOCKER_USER" ]; then echo "ERROR: DOCKER_USER arg required."; exit 1; fi
APP_PREFIX="dcos-stack-"
docker_directories=(api nginx postgres)
for docker_directory in "${docker_directories[@]}"
do
cd $docker_directory
docker build -t ${DOCKER_USER}/${APP_PREFIX}${docker_directory}:latest .
docker push ${DOCKER_USER}/${APP_PREFIX}${docker_directory}:latest
cd ..
done# executed build script
./build-images.sh ericlondon
# reviewing created docker images
docker image ls | egrep -i "ericlondon.*dcos"
ericlondon/dcos-stack-nginx latest 6919414b7569 2 minutes ago 141MB
ericlondon/dcos-stack-api latest 5d6448f3769b 4 minutes ago 351MB
ericlondon/dcos-stack-postgres latest 316536b3f5c4 9 months ago 235MBI created an example pod JSON file for the three containers. file: rails-stack/rails-stack-pod.json
{
"id": "/rails-stack",
"containers": [
{
"name": "api",
"resources": {
"cpus": 0.1,
"mem": 128,
"disk": 0
},
"exec": {
"command": {
"shell": "/api/bin/start-rails.sh"
}
},
"image": {
"kind": "DOCKER",
"id": "ericlondon/dcos-stack-api:latest",
"forcePull": true
},
"endpoints": [
{
"name": "rails-stack-api",
"containerPort": 3000,
"hostPort": 0,
"protocol": [
"tcp"
],
"labels": {
"VIP_0": "/rails-stack:3000"
}
}
],
"environment": {
"POSTGRES_PASSWORD": "postgres",
"POSTGRES_USER": "postgres",
"POSTGRES_HOST": "localhost",
"RAILS_ENV": "development",
"RAILS_PORT": "3000",
"POSTGRES_PORT": "5432"
}
},
{
"name": "postgres",
"resources": {
"cpus": 0.1,
"mem": 128,
"disk": 0
},
"image": {
"kind": "DOCKER",
"id": "ericlondon/dcos-stack-postgres:latest",
"forcePull": true
},
"endpoints": [
{
"name": "rails-stack-postgres",
"containerPort": 5432,
"hostPort": 0,
"protocol": [
"tcp"
],
"labels": {
"VIP_0": "/rails-stack:5432"
}
}
],
"environment": {
"POSTGRES_PASSWORD": "postgres",
"POSTGRES_USER": "postgres"
}
},
{
"name": "nginx",
"resources": {
"cpus": 0.1,
"mem": 128,
"disk": 0
},
"exec": {
"command": {
"shell": "/start-nginx.sh"
}
},
"image": {
"kind": "DOCKER",
"id": "ericlondon/dcos-stack-nginx:latest",
"forcePull": true
},
"endpoints": [
{
"name": "rails-stack-nginx",
"containerPort": 80,
"hostPort": 0,
"protocol": [
"tcp"
],
"labels": {
"VIP_0": "/rails-stack:80"
}
}
],
"environment": {
"API_HOST": "localhost",
"API_PORT": "3000"
}
}
]
}Deploying the Marathon Pod and testing container functionality
# Add marathon pod
dcos marathon pod add rails-stack-pod.json
# get the DCOS task IP address of nginx
service_ip=$(dcos task | egrep -i "nginx.*rails-stack" | awk '{print $2}')
# CURL nginx endpoint which reverse proxies to Rails API
curl http://$service_ip/api/people 2>/dev/null | jq '.[0]'
{
"id": 1,
"first_name": "Eric",
"last_name": "London",
"created_at": "2019-02-24T22:19:43.934Z",
"updated_at": "2019-02-24T22:19:43.934Z"
}Viewing the Rails stack service in DCOS
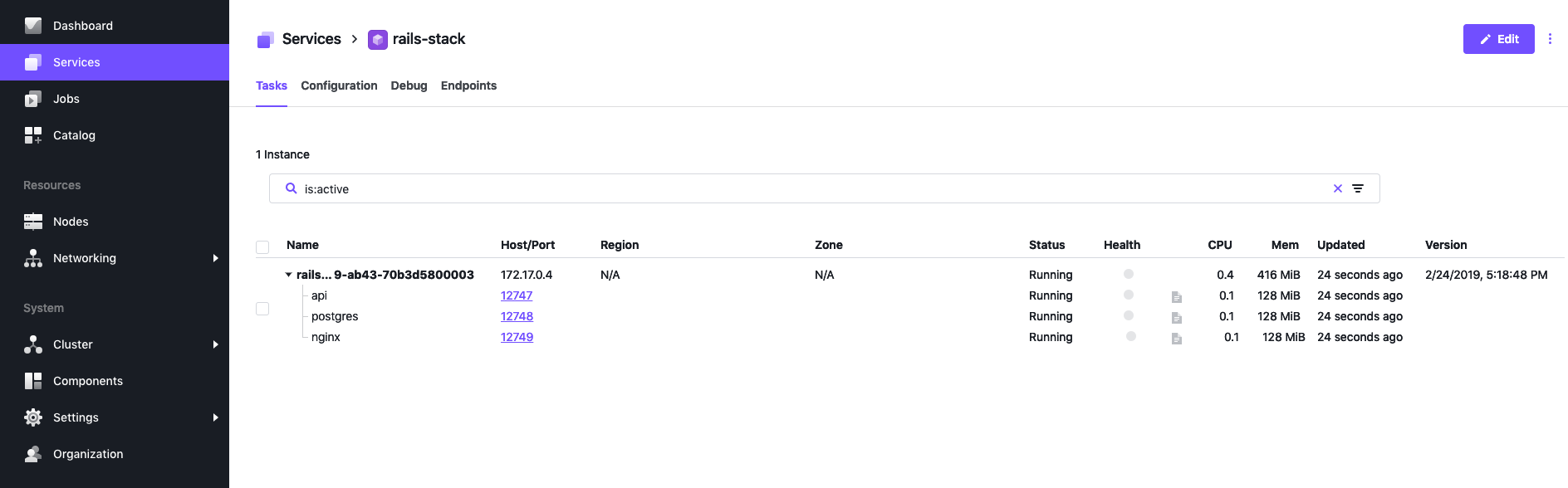
…Next part coming soon!