Create an iOS Swift app to send your location to a Rails API and display on Google Maps
In this post I’ll share a proof of concept project I worked on to create a Swift iOS application to track a user’s location and send the data back to a Rails API. I thought it would be interesting to tinker with a lot of geolocation data and display it back to the user. For this post I decided to simply display the data on a Google Map using the directions API.
Part 1: the Rails backend
Initial project setup:
# create directory and RVM files:
mkdir location_tracker
echo ruby-2.3.1 > location_tracker/.ruby-version
echo location_tracker > location_tracker/.ruby-gemset
cd location_tracker
# when I started this project I was using Rails 4
gem install rails
rails new -d postgresql --skip-test-unit .
# setup database
rake db:create && db:migrateAdd Ruby gems, edit file: Gemfile, add:
# my GitHub repo has all the related ActiveAdmin files but I'm leaving that out of this post
gem 'activeadmin', github: 'activeadmin'
gem 'devise'
gem 'geocoder'
gem 'puma'
gem 'redis'Execute bundle install to install the gems.
Ran the geocoder generator: rails generate geocoder:config. The geocoder gem is used to look up addresses from latitude and longitude. You’ll need to add an ENV variable for your Google Maps API key. Modified file: config/initializers/geocoder.rb
Geocoder.configure(
api_key: ENV.fetch('LOCATION_TRACKER_GOOGLE_API_KEY'),
use_https: true,
cache: Redis.new,
)Created the User model via devise generator.
rails generate devise User
rake db:migrateCreated a migration for the location payloads. This is the table that will contain the data sent from iOS. new file: migrate/20160630145853_create_location_payloads.rb
class CreateLocationPayloads < ActiveRecord::Migration
def change
create_table :location_payloads do |t|
t.latitude, :float, null: false
t.longitude, :float, null: false
t.address, :string
t.timestamp_at, :datetime, null: false
t.speed, :float, null: false
t.references, :user, null: false, index: true, foreign_key: true
t.timestamps null: false
end
end
endExecute rake db:migrate to create the new table.
Edit the user model to add model association, edit file: app/models/user.rb
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
# Include default devise modules. Others available are:
# :confirmable, :lockable, :timeoutable and :omniauthable, :recoverable
devise :database_authenticatable, :registerable,
:rememberable, :trackable, :validatable
has_many :location_payloads
endEdit the location payload model to add the geocoder config and model association, edit file: app/models/location_payload.rb
class LocationPayload < ActiveRecord::Base
reverse_geocoded_by :latitude, :longitude
after_validation :reverse_geocode
belongs_to :user
endCreate a new API controller to receive the location payloads, new file: app/controllers/api/location_payloads_controller.rb
class Api::LocationPayloadsController < ApplicationController
skip_before_filter :verify_authenticity_token
def create
lp_params = location_payload_params
uuid = lp_params.delete :uuid
email = "#{uuid}@example.com".downcase
user = User.where(email: email).first
if user.blank?
password = SecureRandom.hex
user = User.create(email: email,
password: password,
password_confirmation: password)
end
user.location_payloads.create! lp_params
render json: true
end
private
def location_payload_params
required_params = %i(uuid latitude longitude timestamp_at speed)
required_params.each { |p| params.require(p) }
params.permit required_params
end
endAdd create route for location payloads, edit file: config/routes.rb
Rails.application.routes.draw do
# devise_for :admin_users, ActiveAdmin::Devise.config
# ActiveAdmin.routes(self)
# devise_for :users
namespace :api do
resources :location_payloads, only: :create
end
endExecute rails s -b 0.0.0.0 to start the web server (Puma).
Part 2: iOS Swift app code
Now that the backend is ready to receive the location payloads, we’ll move onto the iOS code. I created a new project in Xcode: iOS Single View application, product name: “Location Tracker”, Language: Swift, Devices: Universal.
In the application’s Capabilities section, I enabled Location updates in the background modes. In the Info section, under Custom iOS Target Properties, section: Required background modes, “App registers for location updates” should be included. In addition, I added keys “Privacy - Location Always Usage Description” and “Privacy - Location When In Use Usage Description” with the values “Location is required.”
I dumped all the location services code in the ViewController.swift file:
import UIKit
import CoreLocation
class ViewController: UIViewController, CLLocationManagerDelegate {
var locationManager: CLLocationManager!
var device_uuid: String = ""
var api_host: String = ""
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
// initialize the location manager
locationManager = CLLocationManager()
locationManager.delegate = self
locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest
locationManager.allowsBackgroundLocationUpdates = true
// request location services authorization
if CLLocationManager.authorizationStatus() == .NotDetermined {
locationManager.requestAlwaysAuthorization()
}
// enable location services (choose constant polling or significant changes)
if CLLocationManager.locationServicesEnabled() {
// CLLocationManager.significantLocationChangeMonitoringAvailable()
// locationManager.startUpdatingLocation()
locationManager.startMonitoringSignificantLocationChanges()
}
// get the device uuid
device_uuid = UIDevice.currentDevice().identifierForVendor!.UUIDString
// ngrok, prod url, etc:
api_host = "10.0.1.4:3000"
}
override func didReceiveMemoryWarning() {
super.didReceiveMemoryWarning()
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didChangeAuthorizationStatus status: CLAuthorizationStatus) {
if status == .AuthorizedAlways {
// locationManager.startUpdatingLocation()
locationManager.startMonitoringSignificantLocationChanges()
}
}
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
// get location
let location:CLLocation = locations[locations.count-1]
// create NSURL request
let url:NSURL = NSURL(string: "http://" + api_host + "/api/location_payloads")!
let request:NSMutableURLRequest = NSMutableURLRequest(URL:url)
request.HTTPMethod = "POST"
// create request body
var httpRequestBody = "uuid=" + self.device_uuid
httpRequestBody += "&latitude=" + String(location.coordinate.latitude)
httpRequestBody += "&longitude=" + String(location.coordinate.longitude)
httpRequestBody += "×tamp_at=" + String(location.timestamp)
httpRequestBody += "&speed=" + String(location.speed)
request.HTTPBody = httpRequestBody.dataUsingEncoding(NSUTF8StringEncoding)
let session = NSURLSession.sharedSession()
let task = session.dataTaskWithRequest(request) { (
let data, let response, let error) in
// debug:
// print(data)
// print(response)
// print(error)
}
task.resume()
}
}At this point, I plugged in my iPhone 6 and built/ran the app for my device. After accepting the request to run location services, it opened to a white screen and started sending my location to the Rails API.
Part 3: Google Maps integration
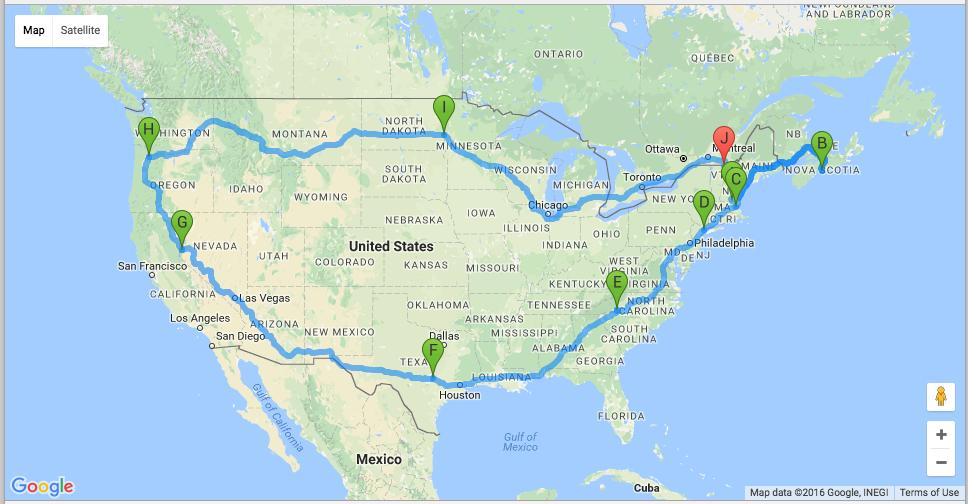
For sake of generating a neat screenshot for this post, and hiding my personal GPS coordinates, I decided to seed some data. Edit file: db/seeds.rb
user = User.create!(email: "#{SecureRandom.uuid}@example.com", password: 'password')
user.location_payloads.create!([
{timestamp_at: Time.now, speed: 0, latitude: 42.765399, longitude: -71.467564}, # Nashua, NH
{timestamp_at: Time.now, speed: 0, latitude: 42.346676, longitude: -71.097218}, # Fenway
{timestamp_at: Time.now, speed: 0, latitude: 40.825629, longitude: -73.930238}, # Yankee Stadium
{timestamp_at: Time.now, speed: 0, latitude: 35.292351, longitude: -81.535646}, # Eastbound & Down
{timestamp_at: Time.now, speed: 0, latitude: 30.267153, longitude: -97.743061}, # Austin, TX
{timestamp_at: Time.now, speed: 0, latitude: 39.529633, longitude: -119.813803}, # Reno 911
{timestamp_at: Time.now, speed: 0, latitude: 45.523062, longitude: -122.676482}, # Portlandia
{timestamp_at: Time.now, speed: 0, latitude: 46.877186, longitude: -96.789803}, # Fargo
{timestamp_at: Time.now, speed: 0, latitude: 44.665206, longitude: -63.567743}, # Trailer Park Boys
{timestamp_at: Time.now, speed: 0, latitude: 44.966741, longitude: -72.13829}, # Super Troopers
])Executed rake db:seed to seed my database.
Created a new API route to visualize the locations for a user, edit file: config/routes.rb
Rails.application.routes.draw do
# ...snip...
resources :users, only: :show do
resources :locations, only: :index
end
endCreated the new controller, file: app/controllers/locations_controller.rb
class LocationsController < ApplicationController
def index
@api_key = ENV.fetch('LOCATION_TRACKER_GOOGLE_API_KEY')
@location_payloads = User.find(user_id)
.location_payloads.select(:latitude, :longitude, :address).order(id: :asc)
end
private
def user_id
params.require(:user_id)
end
endAdded a simple ERB view to create a map container div, output the location data as JSON, and embed the Google Maps API key, file: app/views/locations/index.html.erb
<div id='map'></div>
<script>
(function($){
"use strict";
window.LocationMapper.locations = <%= @location_payloads.to_json.html_safe %>;
})();
</script>
<script async defer src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?key=<%= @api_key %>&callback=window.LocationMapper.createMap"></script>Added some CSS to make the map div fullscreen, edit file: app/assets/stylesheets/application.css
html, body {
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
}
#map {
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
}And last, I added a new JS file to render the location payloads using the Google Maps API directions service, new file: app/assets/javascripts/locations.js
(function($){
"use strict";
window.LocationMapper = new function() {
this.locations = [];
this.createMap = function() {
var directionsService = new google.maps.DirectionsService;
var directionsDisplay = new google.maps.DirectionsRenderer;
var map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'));
directionsDisplay.setMap(map);
var waypoints = [];
for (var i = 0; i < this.locations.length; i++) {
waypoints.push({
location: new google.maps.LatLng(this.locations[i].latitude, this.locations[i].longitude),
stopover: true
});
}
var origin = waypoints.shift().location;
var destination = waypoints.pop().location;
directionsService.route({
origin: origin,
destination: destination,
waypoints: waypoints,
optimizeWaypoints: true,
travelMode: 'DRIVING'
}, function(response, status) {
if (status === 'OK') {
directionsDisplay.setDirections(response);
// debug output
var route = response.routes[0];
for (var i = 0; i < route.legs.length; i++) {
console.log(route.legs[i]);
}
} else {
window.alert('Directions request failed due to ' + status);
}
});
}
}
})();I browsed to http://10.0.1.4:3000/users/1/locations to see: